The Ontology for Linked Open University Data (OLOUD) is a practical approach to model the education activities of a typical Hungarian university. OLOUD aims to integrate data from several sources and provide personal timetables, course-, subject-, curriculum information and other types of help for students and lecturers.
The following diagram summarizes the major concepts for university students and teachers in Hungary:
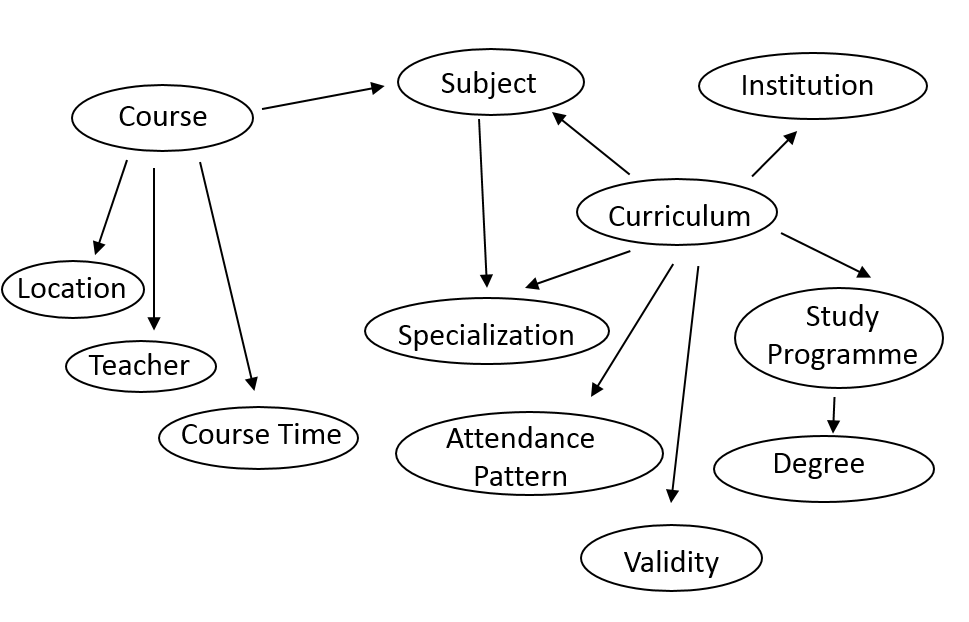
Though the Bologna Process ensures a certain level of compatibility for education systems in the EU, this does not reach deeper constructs of the educational model. We found that especially the meanings of course, subject and study programme are quite different in currently available models. A short summary of how these terms are interpreted in Hungarian education is the following.
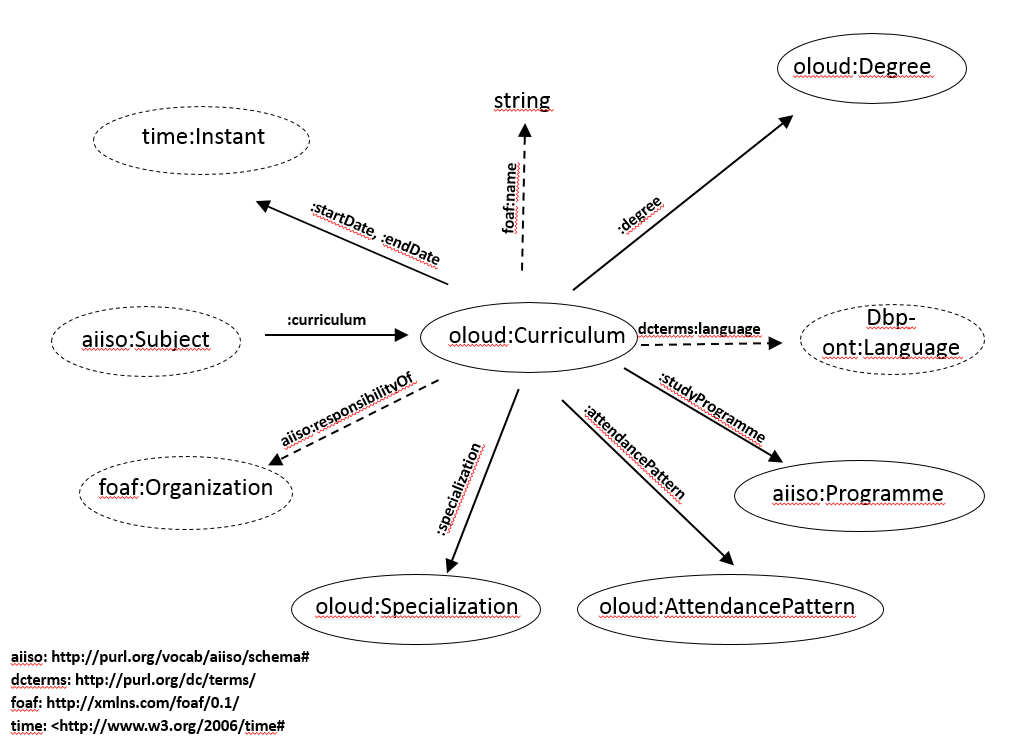
After enrolling to the university each student is assigned to a Curriculum, which is a set of Subjects and their relations (i.e. dependencies among the subjects). Curriculum might specify Specializations which are sets of optional subjects. A Curriculum is in many-to-one relationship with a Study Programme (e.g. Computer Science Engineer), offered by the university. Each Curriculum has a specific Attendance Pattern (full-time, part-time, correspondence, etc.), and a result as a specific Degree (BSc, MSc, BA, MA, PhD, etc.). A Study Programme determines the qualification that a student will get after the successful completion of his studies. A Study Programme must be accredited by an external body. The curriculum is the specification how the Study Programme can be completed. A Curriculum is valid for a given time interval, meaning that a student can be assigned to it only if his enrollment time falls into this period of time. For each Subject there is an Organizational Unit responsible for it. Courses are advertised based on a Subject, have temporal (Course Time) and spatial (Location) attributes and one or more assigned Teacher(s). Additionally, learning materials (Learning Resource) can be assigned to specific courses and subjects.
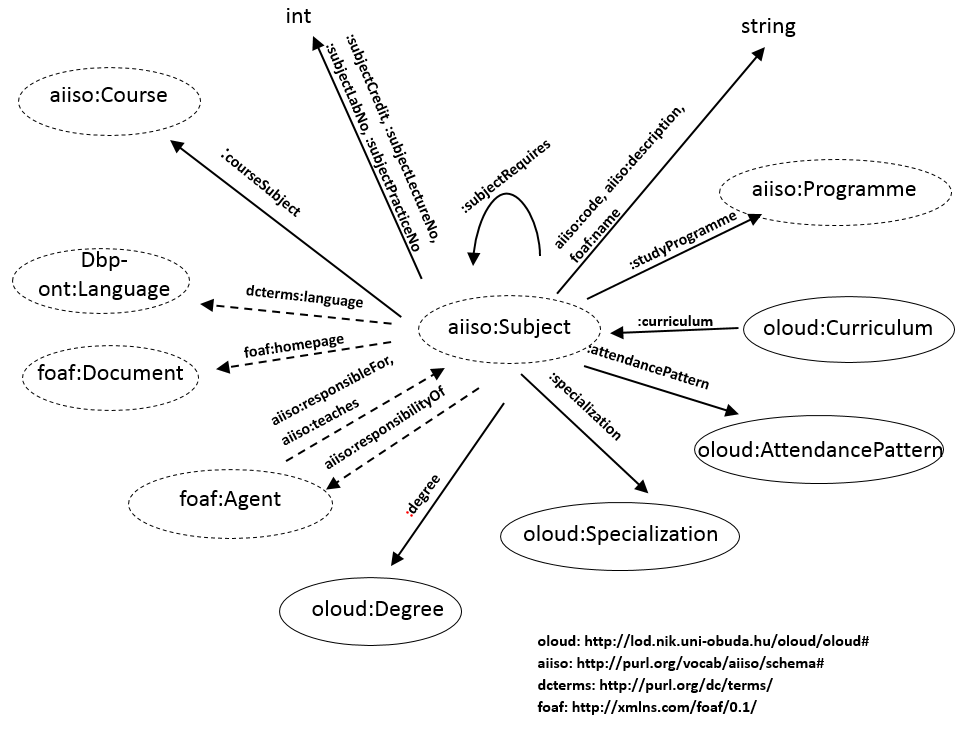
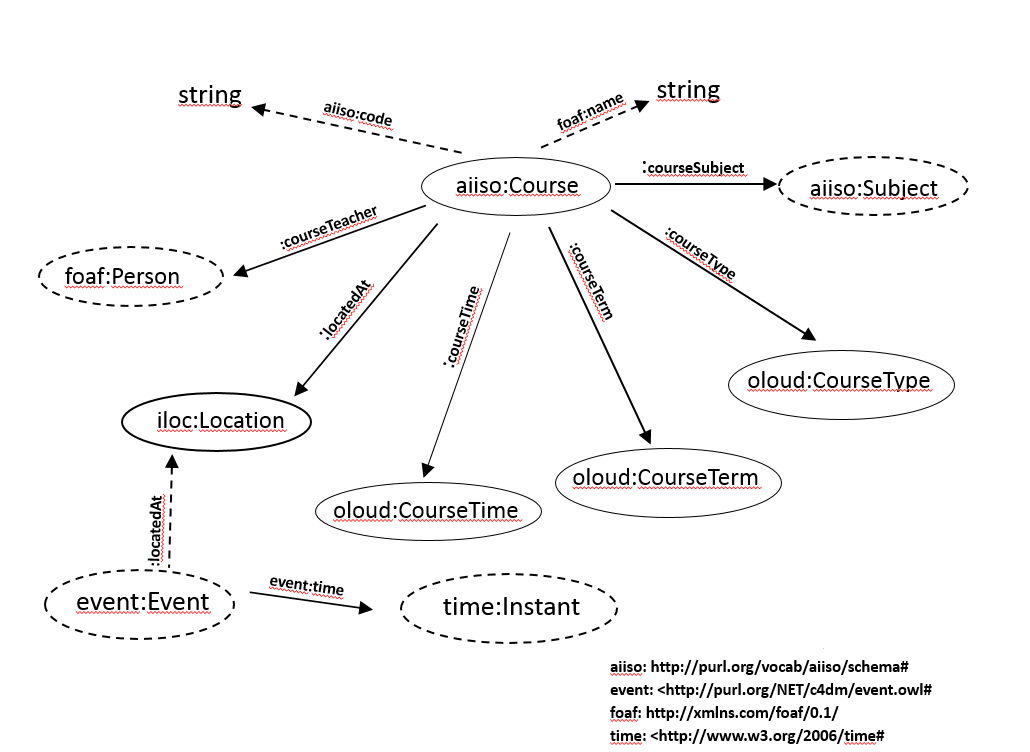
In the case of Hungarian universities, it is crucial to understand the difference between Subjects and Courses. Course is the elementary unit of the educational process, where date, location, teacher and students are assigned. Course is the framework which has a specific training type (like lecture, practice or seminar) and has some requirements that students have to complete. Subject is a higher level component of the training process, it is the unit of the curriculum with a specified training content, and fulfillment is rewarded with a number of credits. It may contain more courses, which all must be completed for the completion of a subject.
The following is a diagram of the OLOUD classes and properties regarding the Curriculum concept:
The following is a diagram of the OLOUD classes and properties regarding the Subject concept:
The following is a diagram of the OLOUD classes and properties regarding the Course concept:
The OLOUD ontology consists of two modules: OLOUD-BASE and OLOUD-TIME. The former describes all the university related concepts, uses the prefix oloud and namespace http://lod.nik.uni-obuda.hu/oloud/oloud#. The latter provides the necessary classes and properties to describe course time data as recurring events, uses the prefix otime and namespace http://lod.nik.uni-obuda.hu/oloud/otime#. OLOUD uses iLOC ontology for indoor navigation and indoor location description tasks.
Download OLOUD-BASE module of the ontology in Turtle format.
Download OLOUD-TIME module of the ontology in Turtle format.